Strategies Box |
The Strategies box:
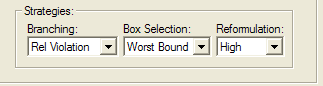
allows you to control three strategies used by the global solver: Branching, Box Selection and Reformulation.
The Branching strategy consists of six options to use when branching on a variable for the first time:
| • | Absolute Width, |
| • | Local Width, |
| • | Global Width, |
| • | Global Distance, |
| • | Absolute Violation, and |
| • | Relative Violation. |
The default setting for Branching is Relative Violation.
The Box Selection option specifies the strategy to use for choosing between all active nodes in the global solver’s branch-and-bound tree. The choices are: Depth First and Worst Bound, with the default being Worst Bound.
The Reformulation option sets the degree of algebraic reformulation performed by the global solver. Algebraic reformulation is critical for construction of tight, convex sub-regions to enclose the nonlinear and nonconvex functions. The available settings are None, Low, Medium and High, with High being the default.
